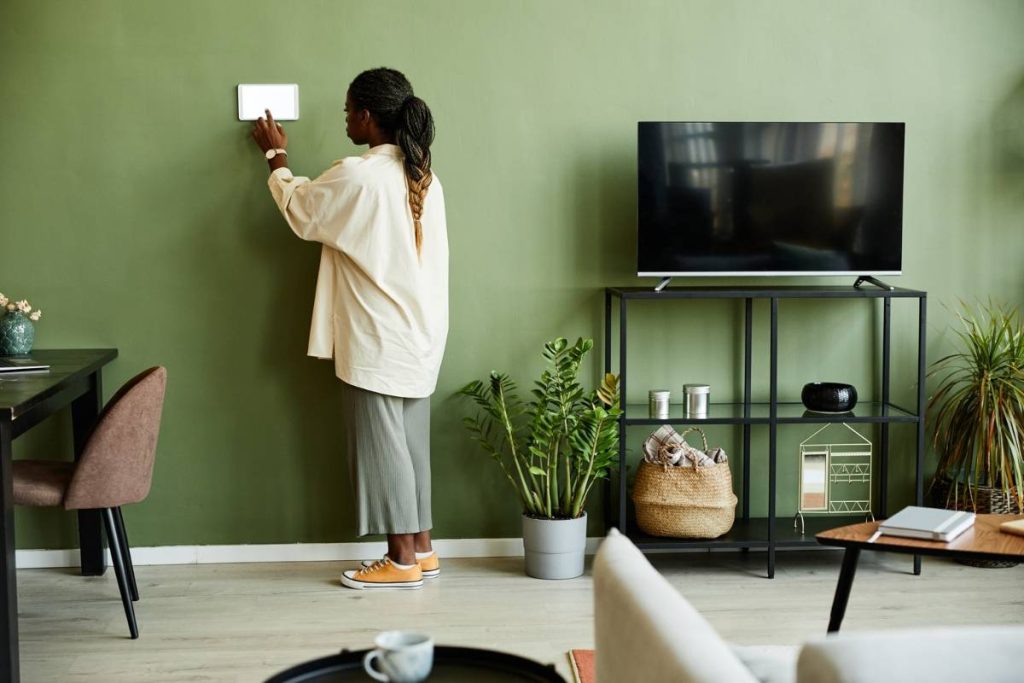
Smart heating and air conditioning systems are reshaping how homes handle comfort, efficiency, and control. Rather than relying on reactive or manual processes, these systems introduce more intentional climate management.
They respond to behavior patterns, environmental conditions, and even voice commands. This article highlights eight impactful benefits of smart HVAC setups that go beyond the usual temperature tweaks.
1. Customization Through Smart Cooling Features
Modern systems don’t operate on fixed schedules alone. They adapt. Smart cooling features let users fine-tune how and when different rooms receive airflow.
Instead of cooling an entire house unnecessarily, the system can focus on occupied spaces or rooms that retain heat longer.
This level of targeting comes from integrated sensors and usage history, which shape more responsive routines. It also reduces energy use during off-hours, avoiding the overwork that shortens an air conditioner’s lifespan.
2. Seamless Integration with Home Automation
Connecting heating and cooling systems to a home automation setup reduces the need for constant input. Schedules can be built around daily routines, such as gradually lowering the temperature during sleep hours or starting the heating system shortly before the alarm goes off.
These adjustments happen automatically, often triggered by time, motion, or occupancy sensors.
The HVAC system can also respond when someone arrives home, adjusting the settings without requiring manual changes. Coordination with other smart devices, such as blinds that close during peak sunlight or lighting that shifts with temperature preferences, supports a stable indoor environment throughout the day.
3. Flexible Control Options
Users no longer have to rely solely on thermostats. Smart HVAC systems often include mobile app controls, which allow adjustments from anywhere with internet access. For households with varying schedules, this flexibility keeps indoor conditions aligned with real-time needs.
The same applies to voice activation features, which support hands-free commands through smart speakers. These controls help reduce overuse by making quick changes more accessible, whether you’re in the kitchen or away from home.
4. Lower Operational Costs Through Efficient Performance
Energy-efficient performance reflects both the design of the equipment and its operating patterns. Smart heating and cooling units learn over time and use data to make fewer, more effective adjustments. That means less frequent cycling, better distribution, and reduced reliance on manual settings.
Households using this kind of system often see a noticeable decrease in utility costs, not just from savings in energy, but from reduced wear on parts.
5. Predictive Maintenance and System Insights
Traditional maintenance often depends on guesswork or visible failure. Smart HVAC systems track their own performance using internal sensors and integrated diagnostics. When something drifts out of range, such as a circuit board running hot or a filter becoming clogged, alerts are sent directly to the user.
This proactive approach shortens repair times, minimizes system stress, and allows for AC maintenance or furnace repair before a breakdown occurs.
6. Smarter Use of Household Energy
A high-efficiency furnace paired with a smart thermostat collects data that can be used to understand energy use. Smart setups often sync with a power meter to better understand when the home draws the most energy and what activities contribute most to it.
This feedback informs choices about scheduling, zoning, and usage limits. The result is a home heating strategy that’s not only reactive but data-informed, especially during peak usage periods.
7. Simplified HVAC Services and Troubleshooting
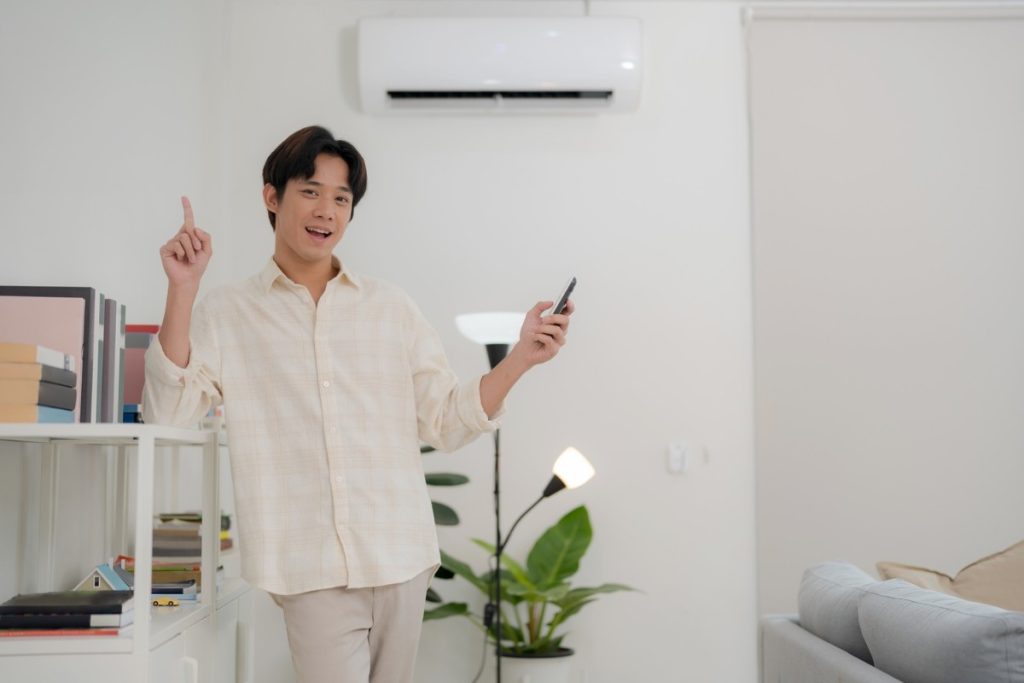

For homeowners, diagnosing HVAC problems used to mean calling for help and waiting. With smart technology, many systems now log activity and provide real-time diagnostics. HVAC services can access this information in advance, making emergency repairs faster and more targeted.
In some cases, remote access allows technicians to resolve minor issues without stepping foot on the property. This shift changes how people approach HVAC maintenance and system replacement.
8. Broader Ecosystem Compatibility
Smart HVAC units increasingly operate within larger ecosystems of connected tools and platforms. Systems that work with voice assistants, third-party sensors, and smart appliances allow for coordinated actions.
For instance, a cooling system might reduce output once the oven switches off, or a heating system may pause temporarily when indoor humidity rises.
Smart home protocol support enables these actions, allowing better alignment across multiple devices without extra manual adjustments.
In Summary
Smart heating and cooling systems use data, usage patterns, and connected tools to manage indoor environments. These systems use elements like control panels, Wi-Fi connectivity, and smart sensors to regulate air flow and temperature in practical, flexible ways.
Whether it’s monitoring outdoor components for efficiency or using a Wi-Fi-operated smart switch to schedule run times, every part contributes to more sustainable, predictable comfort.
Incorporating features such as indoor temperature control and predictive diagnostics, modern HVAC setups prioritize user needs with accuracy.
From energy-efficient heating in winter to cooling equipment that adapts in real time, these innovations help reduce waste, improve longevity, and support informed decisions. Smart HVAC systems aren’t about pushing buttons; they’re about reshaping how homes respond to the people living in them.