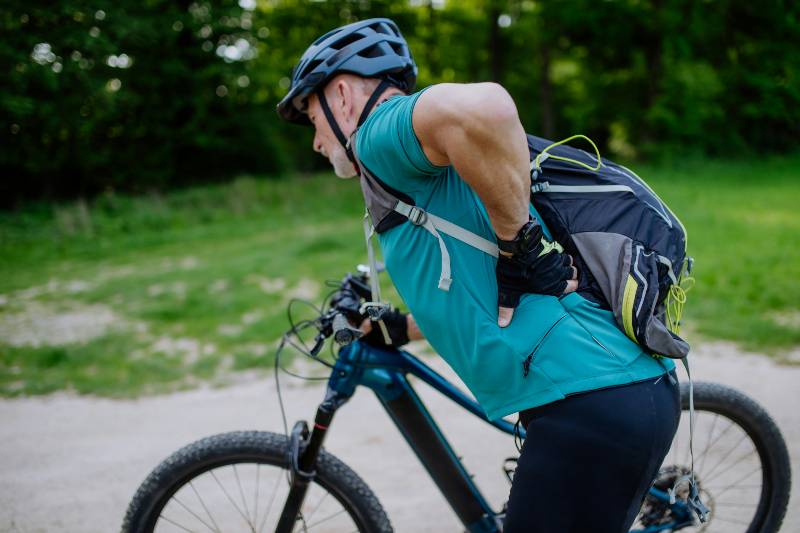
You’re wondering why your back feels like it’s been through a week of tight and stiff planks.
Like many, you might be dealing with back pain, and you suspect that your stiff and tight muscles are the culprits.
Knowing the reasons behind muscle stiffness and how they connect to that nagging pain in your back will give you insights and possibly solutions to this uncomfortable and disruptive issue.
What Causes Stiff and Tight Muscles?
Your muscles can become stiff and tight for a variety of reasons.
Physical activity, or the lack thereof, often plays a key role. When you engage in intense exercise or new physical activities, your muscles work harder than they’re used to, which can lead to stiffness as part of the recovery process.
In contrast, long periods of inactivity can cause muscles to tighten up due to a lack of movement and stretching.
Stress is also a big contributor to muscle tension. In response to stress, your muscles may contract involuntarily, particularly around the neck and back, leading to soreness and stiffness.
Even poor sleep or an uncomfortable mattress can contribute to the problem, as can dehydration, which affects muscle function and flexibility.
Why Stiff and Tight Muscles Can Result in Back Pain?
Back pain is a complex condition that can arise from several physical problems. One common and often overlooked cause of back pain is the presence of stiff and tight muscles.
You may wonder just how this muscle stiffness and tightness translate into the aches you feel in your back. There are many ways in which muscles that are not functioning optimally contribute to back discomfort.
Reduced Range of Motion
When your muscles are stiff and tight, your body compensates by limiting how far you can move. You might notice that bending over to tie your shoes or reaching up to grab something from a shelf has become more difficult.
This reduced range of motion affects how your back muscles and spine work together, making certain movements painful or even impossible. It’s a vicious cycle: the less you move, the stiffer you become, potentially leading to more pain.
Poor Posture
Stiff muscles, especially in the back and shoulders, can force you into unnatural positions. As a result, your posture can take a hit. Whether you’re sitting or standing, your body may lean into a particular stance that relieves the immediate discomfort caused by tight muscles.
However, poor posture is a known cause of back pain, as it puts additional strain on your spine and the muscles that support it.
Muscle Imbalances
Not all muscles tighten up equally, which can lead to imbalances in your musculoskeletal system.
For instance, if your hip flexors are tight but your abdominal muscles are weaker, there’s an increased chance of tilting your pelvis forward. This anterior pelvic tilt can cause a significant strain on your lower back, thus contributing to back pain.
Increased Spinal Compression
Your spine relies heavily on the support and cushioning provided by surrounding muscles and intervertebral discs. When muscles become tight, especially the erector spinae which run along your spine, they can create an excessive amount of pressure on the spine itself.
Over time, increased spinal compression can lead to back pain as the supportive structures are strained beyond their normal function.
Trigger Points and Referred Pain
Tight muscles often harbor trigger points, which are tender knots within the muscle fibers. These knots can cause pain over a larger area, a phenomenon known as referred pain.
Trigger points in the back muscles can refer pain to various regions of the back, intensifying the discomfort you feel.
Circulation Issues
Tight muscles can also impact circulation, reducing the flow of blood and essential nutrients to the muscles. Poor circulation can lead to a buildup of byproducts like lactic acid, which can further irritate muscles and nerve endings, adding to the sensation of pain.
Stress and Emotional Tension
Sometimes back pain is more than just a physical issue. Stress and emotional tension can manifest physically in the body, with the back being a common area for carrying this weight.
When you’re emotionally stressed, your muscles may clench unconsciously.
This ongoing tension in muscles like those in the upper and lower back can lead to persistent back pain. Thus, it’s important to address not only the physical but also the emotional factors that could be contributing to muscle stiffness and associated back pain.
What Stiff and Tight Muscles Can Cause Back Pain?
Muscles across your body play a role in the health of your back. Let’s explore some key muscle groups whose tightness can lead to back pain.
Hip Flexors
The hip flexors are a group of muscles near the top of your thighs that allow you to bend at the waist and lift your knees. Tight hip flexors can pull on the lower back and destabilize your posture, leading to back pain. Especially if you sit for long periods, these muscles are prone to stiffness.
Hamstrings
Your hamstrings run down the back of your thighs. When they’re tight, they can cause a pull on the lower back, and this tension can alter your pelvis’s natural alignment, straining your spine. Stretching the hamstrings is often recommended for people with back pain for precisely this reason.
Rotator Cuff
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder joint. While their primary role is in shoulder movement, tightness here can affect the spine due to the connected muscles running along the back.
When your rotator cuff is stiff, your upper back and neck often compensate for the lack of shoulder mobility, potentially causing upper back pain.
Obliques
The oblique muscles on the sides of your torso play a significant role in twisting motions and maintaining core stability. Tight obliques can restrict trunk mobility, forcing your back to take on more workload, which can induce or aggravate back pain.
Trapezius
This broad muscle extends from your neck to the middle of your back and out to your shoulders. When the trapezius muscle is tight, often due to poor posture or stress, it can result in tension headaches, shoulder pain, as well as stiffness and pain in the back.
Erector Spinae
This group of muscles runs along your spine and helps you stand up straight and arch your back. When the erector spinae become tight, they can lead to a reduced range of motion in the spine and increase the pressure on intervertebral discs, contributing to discomfort and pain in the back.
Intercostal Muscles
These muscles are located between the ribs and assist with breathing. Tightness in the intercostal muscles can restrict chest expansion, leading to shallow breathing.
This lack of full breath movement can increase tension in the upper back and spinal region, thereby leading to or exacerbating back pain.
What Treatment Can Help Relieve Back Pain From Stiff and Tight Muscles?
Finding effective treatments can be a relief for those suffering from back pain caused by stiff and tight muscles. There are various methods to consider, and often a combination approach can yield the best results.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can teach you exercises specifically designed to stretch and strengthen the muscles that support your back. A physical therapist can also work out the kinks in your muscles, improve your range of motion, and advise on proper posture and ergonomics.
Massage Therapy
Massage therapy is excellent for working out tight muscles and improving circulation. A massage therapist can target areas with deep tissue techniques to release muscle tension and promote relaxation, which can help alleviate back pain.
Stretching and Exercise
Regular stretching can help improve flexibility and reduce muscle tightness. Along with stretching, a balanced exercise routine that includes strength training and cardio activity can keep muscles conditioned and less likely to become stiff.
Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat can relax tight muscles, while cold therapy can help reduce inflammation that might be contributing to muscle tension and back pain. It’s important to understand when to use each; typically, heat is beneficial for chronic stiffness, while cold therapy is better for acute injuries.
Stress Reduction Techniques
As stress can tighten muscles, employing stress reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can indirectly relieve muscle tightness and back pain.
Proper Hydration and Nutrition
Maintaining good hydration helps keep the muscle tissue supple, and a balanced diet can provide the nutrients needed for muscle health.
How Long Should You Wait to See a Doctor for Back Pain?
If your back pain is the result of stiff and tight muscles, it may improve with home care efforts such as those mentioned above. However, you need to monitor your condition.
If your back pain is severe, persists for more than a week without any signs of improvement, or is accompanied by other worrying symptoms like numbness or tingling, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional.
Always seek immediate medical attention if back pain develops after a traumatic injury, if it’s associated with trouble urinating, fever, or unintentional weight loss, as these could be signs of a more serious condition.
The general rule is that if your back pain limits your movements or interferes with your daily activities, a doctor’s visit is justified.
Don’t underestimate persistent pain either. If you’re regularly experiencing back pain after participating in certain activities or at specific times of the day, it’s worth getting a professional opinion. Early intervention can often prevent back pain from becoming chronic and may reduce the risk of further injury.
Conclusion
Back pain resulting from stiff and tight muscles is a widespread issue that can stem from various factors such as poor posture, muscle imbalances, and stress.
Understanding the intricacies of why your muscles are tight and how that tightness contributes to your back pain is the first step toward finding relief.
Treatments like physical therapy, massage, proper exercise, and stress reduction can provide significant improvements.