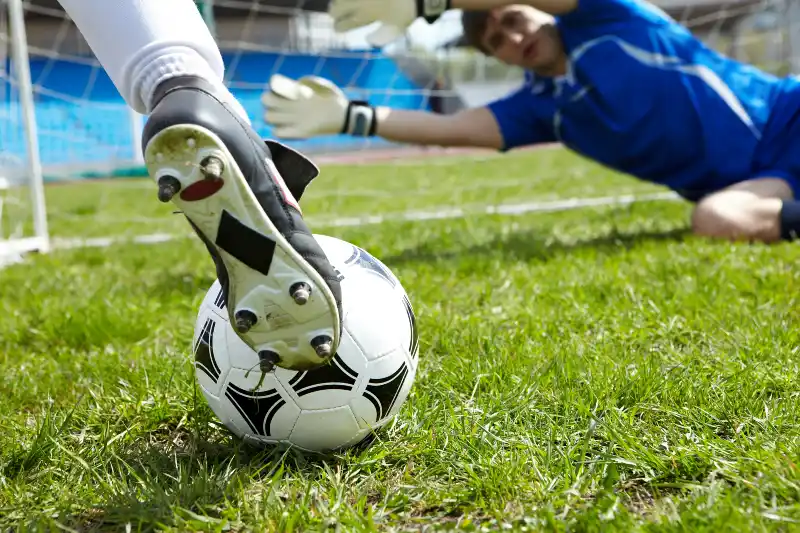
Knowing the duration of the FIFA World Cup soccer games can be quite helpful if you’re planning to join the global community of fans cheering on their favorite teams, or simply if you’re curious about how soccer or football (known outside North America) keeps time.
You might be asking yourself: How long should I commit to watching a game? Can games go on longer than expected?
How Long Is a World Cup Soccer Game?
A standard World Cup soccer game is divided into two halves, each lasting 45 minutes, with a 15-minute halftime interval separating them. Therefore, in theory, the total time of a match is 90 minutes plus halftime, adding up to 105 minutes or 1 hour and 45 minutes.
However, this duration can be extended for various reasons due to specific aspects of the game’s flow and rules.
Factors Influencing the Time of a World Cup Soccer Game
When you sit down to enjoy a World Cup match, several factors can affect the length of the game, extending beyond the initial 90 minutes of play time.
1. Stoppage Time
One of the most common factors is known as stoppage time or injury time. The clock in soccer does not stop for most events that can cause delays in other sports, such as injuries, substitutions, or when the ball goes out of play.
Therefore, the referee adds extra time at the end of each half to account for these interruptions. The amount of stoppage time is at the referee’s discretion, but it typically ranges from 1 to 5 minutes per half.
2. VAR Reviews
The Video Assistant Referee (VAR) system can also impact the length of the game. Introduced to the World Cup in 2018, VAR is used to review decisions made by the head referee with video footage.
This can extend the game time, as play is often stopped to allow referees to consult video replay for critical decisions such as goals, penalty calls, direct red card incidents, and mistaken identity in awarding cards.
3. Extra Time and Tiebreakers
In the knockout stages of the World Cup, games that end in a draw after 90 minutes move into extra time, consisting of two 15-minute periods. There is a brief pause between these periods but no formal halftime.
This brings the total playing time to 120 minutes. If the match is still tied after this additional half hour, it is decided by a penalty shootout.
4. Delays and Suspensions
Rarely, matches can be delayed due to weather conditions, such as heavy rain or lightning, that make the field unplayable or put players and fans at risk. Games can also be suspended due to extraordinary events, such as power outages or security concerns.
In these cases, matches may be paused and resumed once conditions are deemed safe, adding a significant amount of time to the overall duration of the game.
5. Substitutions
Substitutions are a typical part of soccer, and each team is allowed a certain number of player changes during the match.
These switches can add to the game’s duration since the clock continues to run while substitutions are made, and additional stoppage time is added to compensate for these breaks in play.
6. Celebrations and Time-Wasting
Goals are eagerly celebrated in soccer, but they also take time. Players rejoicing after scoring can add minutes to a match, as can actions deemed as time-wasting by the team in the lead—like taking longer to set up for free kicks or goal kicks.
The referee takes note of these instances and can extend the stoppage time accordingly.
How Does Overtime Work in Soccer?
Understanding overtime, more formally known as extra time in the context of the World Cup, is crucial, especially during the knockout stages—where there has to be a winner.
Should the game be tied at the end of regular play, the teams will engage in two additional 15-minute halves with a short, approximately 1-minute break in between, but no substitutions are allowed during this break. This takes the total potential match time to 120 minutes.
Penalty Shootouts
If the deadlock isn’t broken during extra time, the winner is decided through a penalty shootout. Teams take turns kicking from the penalty spot, with five shots each, and the team with the most goals after these five rounds wins.
If the score is still level, the shootout proceeds to a sudden death format. The penalty process can add a dramatic 20 minutes or more to the game’s total length.
Impact of Referee’s Whistle
It’s worth noting that the referee’s whistle ultimately starts and ends the game. The match isn’t over until the referee blows the final whistle, which typically occurs after the completion of the announced stoppage time.
However, if there’s an ongoing play that could change the match’s outcome, such as an attack
leading towards a potential goal, the referee might allow it to conclude before signaling the end of the match. This can sometimes add a minute or so to the advertised stoppage time, prolonging the suspense for fans and players alike.
Injuries
Injuries are a frequent occurrence in the high-impact play of World Cup soccer. When a player is injured, the match clock continues to run as medical staff assess the situation and provide treatment on the field.
To compensate for this interruption, the referee adds the lost time to the end of the half during which the injury occurred. If a player is seriously injured and must be stretchered off the field, this can result in a significant amount of additional stoppage time.
Disciplinary Actions
Confrontations between players, disputes over calls, and the issuance of yellow or red cards can all lead to stoppage of play.
These confrontations and the resolution process take time, during which the match clock does not stop. The referee will add time for these delays at the end of each half.
Corner Kicks and Free Kicks
While not adding as much time as other factors, corner kicks and free kicks can lead to brief stops in play that add up over the course of a match.
Setting up for these plays takes time, as players must position themselves correctly, which often involves discussions with the referee. This organization, along with the actual execution of the kick, can add several minutes over the length of a full soccer match.
Throw-ins and Goal Kicks
Similarly to corner kicks and free kicks, throw-ins and goal kicks are smaller stoppages that contribute to additional time. Players may take their time retrieving the ball for a throw-in or setting up a goal kick to either catch a breath or tactically manage the game’s pace.
These moments are particularly strategic towards the end of a game when the leading team might use such opportunities to slow the game down.
Technical Difficulties
On rare occasions, technical difficulties with the stadium facilities, such as malfunctioning scoreboards or issues with VAR technology, can cause unexpected delays. Although uncommon, they’re yet another factor that can extend the length of a World Cup game.
Conclusion
Now that you’re more familiar with the various elements that influence the duration of World Cup soccer games, you can better plan your viewing schedule.
while a single match is slated to last just over an hour and a half (plus a 15-minute halftime break), the reality can be quite different due to the dynamic nature of the sport and the variables mentioned above.
It’s wise to set aside at least two hours when you plan to watch a World Cup game.