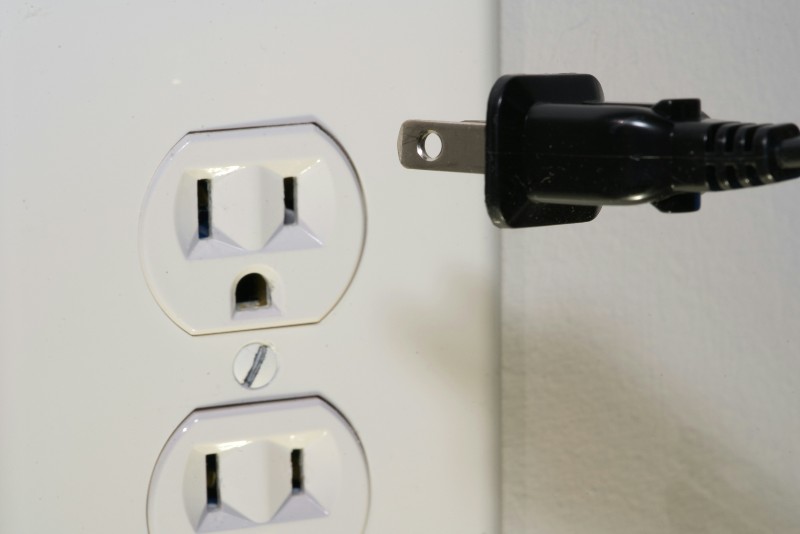
When you plug a cord into an outlet, have you ever noticed the tiny holes on each of the metal prongs and wondered about their purpose?
These holes may seem insignificant at first glance, but they play an important role in the design and functionality of electric plugs.
Their presence is a result of thoughtful engineering aimed at enhancing both safety and production efficiency.
Let’s see the common 4 reasons behind this seemingly minor, yet important feature of electric plugs.
1. Enhance Grip and Reduce Slippage
Safety is a paramount concern in the design of electrical hardware. One primary reason for the two holes on plug prongs is to provide a better grip within the socket.
Inside many outlets, there are small balls or springs that fit snugly into these holes, creating a locked position for the plug.
This secure fit ensures the plug stays in place, reducing the risk of it being partially or completely pulled out accidentally.
A stable connection not only improves safety by maintaining consistent electrical contact but also protects the integrity of both the plug and socket from wear and tear.
2. Manufacturing Efficiency
From a manufacturing standpoint, these holes prove highly beneficial.
During the assembly and quality control stages, machines and workers can use these holes to hold and manipulate the plugs more easily.
A quicker assembly and thorough inspection of each unit become possible as these holes significantly accelerate production lines.
It ensures that the plugs are correctly assembled and meet the required safety standards before they hit the market.
The inclusion of these holes in the prongs can also be seen as a clever design tweak that saves time and resources, facilitating mass production without compromising on quality.
3. Cost Reduction
Incorporating these holes into the design of electric plug prongs can contribute to cost reduction as well.
By removing a tiny bit of metal from each prong, manufacturers can save on material costs when producing millions of units.
Though the savings per plug might be minimal, when scaled up, this can lead to significant reductions in production costs.
4. Historical and Standardization Aspects
The origin of the two holes in plug prongs can also be traced back to historical designs and the evolution of electrical standards. As electric plugs and outlets were standardized over the years, the holes in prongs became commonplace.
They serve as a testament to innovation in electrical engineering, reflecting changes in safety standards, manufacturing practices, and consumer needs.
By understanding the history and the rationale behind standardized features, consumers can appreciate the careful consideration that goes into even the smallest components of our daily technologies.
Moreover, the standardization of the two holes plays a critical role in ensuring compatibility across a wide range of devices and electrical systems.
It harmonizes the design and functionality of plugs and sockets, making it easier for consumers to use products safely and efficiently, regardless of where they are manufactured or used.
This global approach to design standardization helps maintain a level of safety and convenience for users worldwide, demonstrating how thoughtful engineering can lead to universally beneficial outcomes.
When Were the Two Holes Introduced to Electric Plugs?
The design feature of having two holes in the prongs of electric plugs does not have a specific “invention” date. Throughout the 20th century, the design of electrical plugs and sockets, including features like prong holes, became standardized.
In the United States, for example, the two-slot electrical outlet (with one wide slot and one narrow slot for polarized plugs) and the three-prong outlet (adding a round hole for grounding) have been in widespread use since the mid-20th century.
The exact origin of the design feature of the two holes is difficult to attribute to a single inventor or a precise date, largely because it was the result of gradual improvements and innovations in the field of electrical engineering.
However, it’s clear that the early 20th century was a period of significant innovation in electrical plug and socket design, with inventors like Harvey Hubbell leading the way.
Conclusion
The two holes in the prongs of electric plugs represent more than just a peculiar design choice. They are the result of careful consideration of manufacturing efficiency, safety enhancement, cost reduction, and adherence to standardized practices.
These features encapsulate the essence of electrical engineering: a field where every minor detail can have a significant impact on the product’s overall functionality and user safety.
As technology progresses and our needs evolve, the design of electric plugs may continue to change.
However, the principles behind such design choices focused on efficiency, safety, and standardization will likely remain constant, guiding future innovations in the electrical hardware we use every day.
The future may hold wireless electricity, advanced smart plugs, or entirely new standards for electrical connectivity, but the foundational principles seen in the humble design of today’s electric plugs will continue to inspire and inform those advancements.